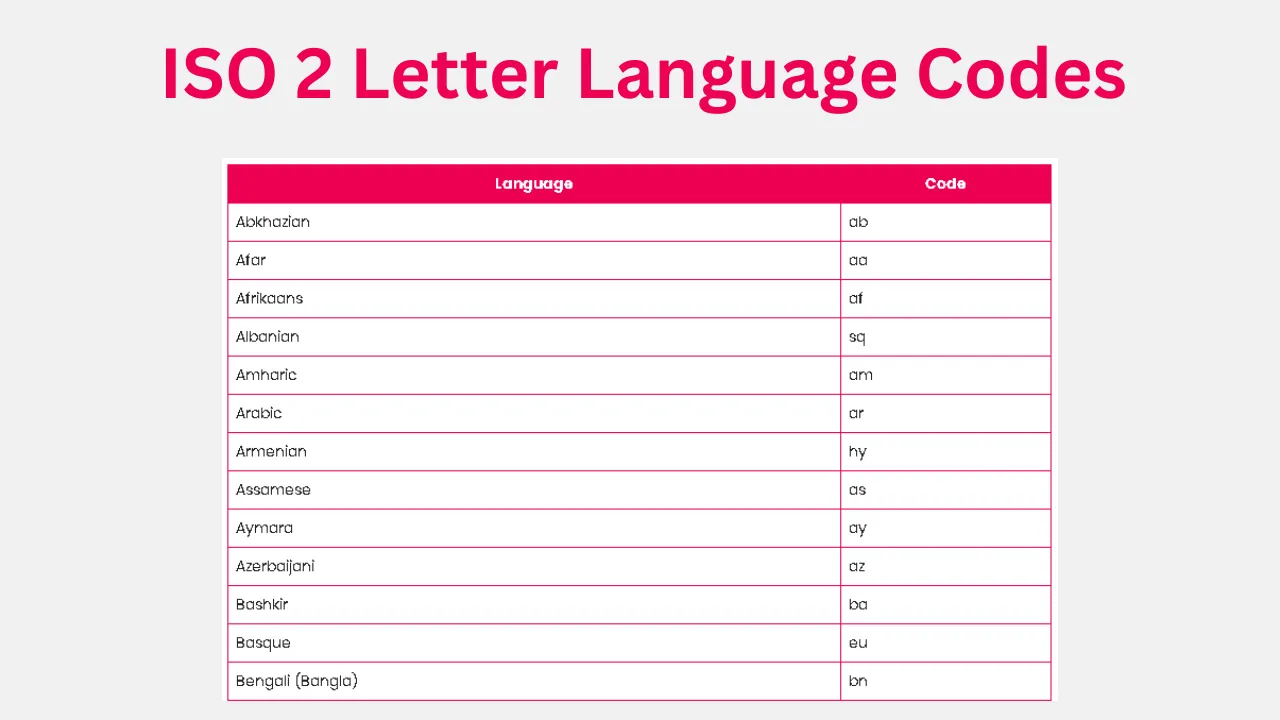
ISO 2 letter language codes, also known as ISO 639-1 codes, are standardized two-letter identifiers for languages established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These codes are widely used in various fields, including linguistics, information technology, and international communication.
Key Features:
- Two-letter format: Each language is represented by a unique two-letter combination.
- Case-insensitive: The codes are not case-sensitive, though they are typically written in lowercase.
- Wide coverage: The system includes codes for major world languages and many less common ones.
- Standardization: Being an ISO standard, these codes are internationally recognized and widely adopted.
Uses:
- Web development: In HTML and XML documents to specify the language of content.
- Bibliographic systems: To identify the language of publications.
- Software localization: To manage different language versions of software.
- International organizations: For efficient communication about language-related matters.
ISO 639-1 Language Codes
ISO 639-1 defines abbreviations for languages:
| Language | ISO Code |
|---|---|
| Abkhazian | ab |
| Afar | aa |
| Afrikaans | af |
| Albanian | sq |
| Amharic | am |
| Arabic | ar |
| Armenian | hy |
| Assamese | as |
| Aymara | ay |
| Azerbaijani | az |
| Bashkir | ba |
| Basque | eu |
| Bengali (Bangla) | bn |
| Bhutani | dz |
| Bihari | bh |
| Bislama | bi |
| Breton | br |
| Bulgarian | bg |
| Burmese | my |
| Byelorussian | be |
| Cambodian | km |
| Catalan | ca |
| Chinese | zh |
| Corsican | co |
| Croatian | hr |
| Czech | cs |
| Danish | da |
| Dutch | nl |
| English, American | en |
| Esperanto | eo |
| Estonian | et |
| Faeroese | fo |
| Fiji | fj |
| Finnish | fi |
| French | fr |
| Frisian | fy |
| Gaelic (Scots Gaelic) | gd |
| Galician | gl |
| Georgian | ka |
| German | de |
| Greek | el |
| Greenlandic | kl |
| Guarani | gn |
| Gujarati | gu |
| Hausa | ha |
| Hebrew | iw |
| Hindi | hi |
| Hungarian | hu |
| Icelandic | is |
| Indonesian | id, in |
| Interlingua | ia |
| Interlingue | ie |
| Inupiak | ik |
| Irish | ga |
| Italian | it |
| Japanese | ja |
| Javanese | jw |
| Kannada | kn |
| Kashmiri | ks |
| Kazakh | kk |
| Kinyarwanda | rw |
| Kirghiz | ky |
| Kirundi | rn |
| Korean | ko |
| Kurdish | ku |
| Laothian | lo |
| Latin | la |
| Latvian, Lettish | lv |
| Lingala | ln |
| Lithuanian | lt |
| Macedonian | mk |
| Malagasy | mg |
| Malay | ms |
| Malayalam | ml |
| Maltese | mt |
| Maori | mi |
| Marathi | mr |
| Moldavian | mo |
| Mongolian | mn |
| Nauru | na |
| Nepali | ne |
| Norwegian | no |
| Occitan | oc |
| Oriya | or |
| Oromo, Afan | om |
| Pashto, Pushto | ps |
| Persian | fa |
| Language | ISO Code |
|---|---|
| Polish | pl |
| Portuguese | pt |
| Punjabi | pa |
| Quechua | qu |
| Rhaeto-Romance | rm |
| Romanian | ro |
| Russian | ru |
| Samoan | sm |
| Sangro | sg |
| Sanskrit | sa |
| Serbian | sr |
| Serbo-Croatian | sh |
| Sesotho | st |
| Setswana | tn |
| Shona | sn |
| Sindhi | sd |
| Singhalese | si |
| Siswati | ss |
| Slovak | sk |
| Slovenian | sl |
| Somali | so |
| Spanish | es |
| Sudanese | su |
| Swahili | sw |
| Swedish | sv |
| Tagalog | tl |
| Tajik | tg |
| Tamil | ta |
| Tatar | tt |
| Telugu | te |
| Thai | th |
| Tibetan | bo |
| Tigrinya | ti |
| Tonga | to |
| Tsonga | ts |
| Turkish | tr |
| Turkmen | tk |
| Twi | tw |
| Ukrainian | uk |
| Urdu | ur |
| Uzbek | uz |
| Vietnamese | vi |
| Volapuk | vo |
| Welsh | cy |
| Wolof | wo |
| Xhosa | xh |
| Yiddish | yi, ji |
| Yoruba | yo |
| Zulu | zu |
It’s important to note that while ISO 639-1 covers a wide range of languages, it doesn’t include codes for every known language. For more comprehensive coverage, ISO 639-2 (three-letter codes) and ISO 639-3 (three-letter codes covering all known languages) are available.
When using these codes, it’s crucial to refer to the official ISO documentation to ensure accuracy, as some codes might not be intuitive (e.g., ‘eu’ for Basque, ‘el’ for Greek).
In the digital age, these codes play a vital role in facilitating multilingual content management and ensuring proper language identification across various platforms and systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about ISO Language Codes
What are these language codes?
These codes are standardized representations of languages, typically consisting of two letters. They are used internationally to identify languages in various contexts.
What is the format of the language codes in the provided list?
The codes in the list are two-letter abbreviations, written in lowercase. For example, “pl” stands for Polish, “pt” for Portuguese, and “es” for Spanish.
How many languages are included in the provided list?
The list contains 49 languages and their corresponding codes.
Are these codes part of a specific standard?
While not explicitly stated, the codes appear to be similar to ISO 639-1 codes, which are two-letter codes used to represent languages. ISO 639-1 codes are typically lowercase.
How are the languages ordered in the list?
The languages are listed in alphabetical order based on their English names.